There are thousands of Satellites orbiting the Earth above Us everyday. And more and more satellites will continued to be launched into space. But not all satellites are the same. They are sent into space for a variety of missions from helping us better our understanding of the universe to protecting our interests as a nation to communication and entertainment. Satellites are classified based on their purpose, orbit, and function. Here are the main types:
1. Communication Satellites
- Purpose: Facilitate telecommunication by relaying signals from one point on Earth to another.
- Examples: TV broadcasting, internet, telephone services.
- Orbit: Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO) is common, but some use Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) or Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
2. Weather Satellites
- Purpose: Monitor Earth's weather and climate.
- Examples: Tracking storms, observing atmospheric conditions, and predicting weather patterns.
- Orbit: Geostationary (for continuous monitoring) or Polar Orbit (for global coverage).
3. Navigation Satellites
- Purpose: Provide positioning, navigation, and timing services.
- Examples: GPS (Global Positioning System), GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou.
- Orbit: Medium Earth Orbit (MEO).
4. Earth Observation Satellites
- Purpose: Observe and monitor Earth's surface for environmental, agricultural, urban, and military purposes.
- Examples: Landsat, Sentinel, Terra.
- Orbit: Low Earth Orbit (LEO), typically polar or sun-synchronous orbit.
5. Scientific Satellites
- Purpose: Conduct scientific research and experiments in space.
- Examples: Hubble Space Telescope, James Webb Space Telescope, various Earth and space science missions.
- Orbit: Varies, depending on mission goals (LEO, MEO, or even farther in deep space).
6. Reconnaissance (Spy) Satellites
- Purpose: Gather intelligence and surveillance data for military or governmental use.
- Examples: Imaging and radar reconnaissance.
- Orbit: Low Earth Orbit (LEO) for detailed imaging orbits.
7. Space Exploration Satellites
- Purpose: Explore celestial bodies, gather data, and relay information back to Earth.
- Examples: Mars rovers, lunar orbiters, interplanetary missions like Voyager.
- Orbit: Various, depending on the mission (e.g., Mars orbit, lunar orbit, deep space trajectories).
8. CubeSats and NanoSats
- Purpose: Small, often low-cost satellites used for scientific research, technology demonstrations, or educational purposes.
- Examples: Various university-led missions, commercial tech demos.
- Orbit: Typically Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
9. Space Station Modules
- Purpose: Habitation, research, and operations in space.
- Examples: International Space Station (ISS), Tiangong.
- Orbit: Low Earth Orbit (LEO).
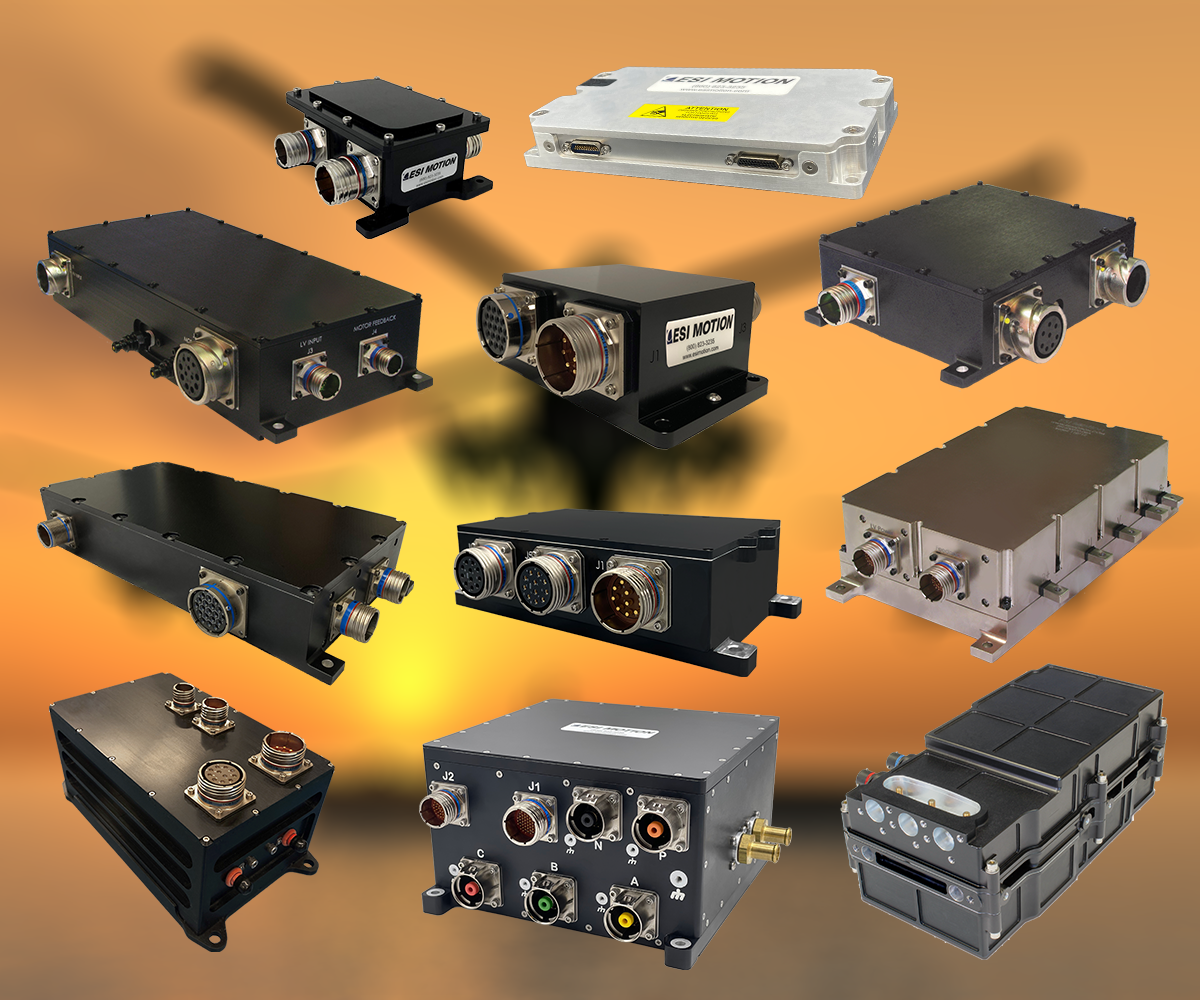
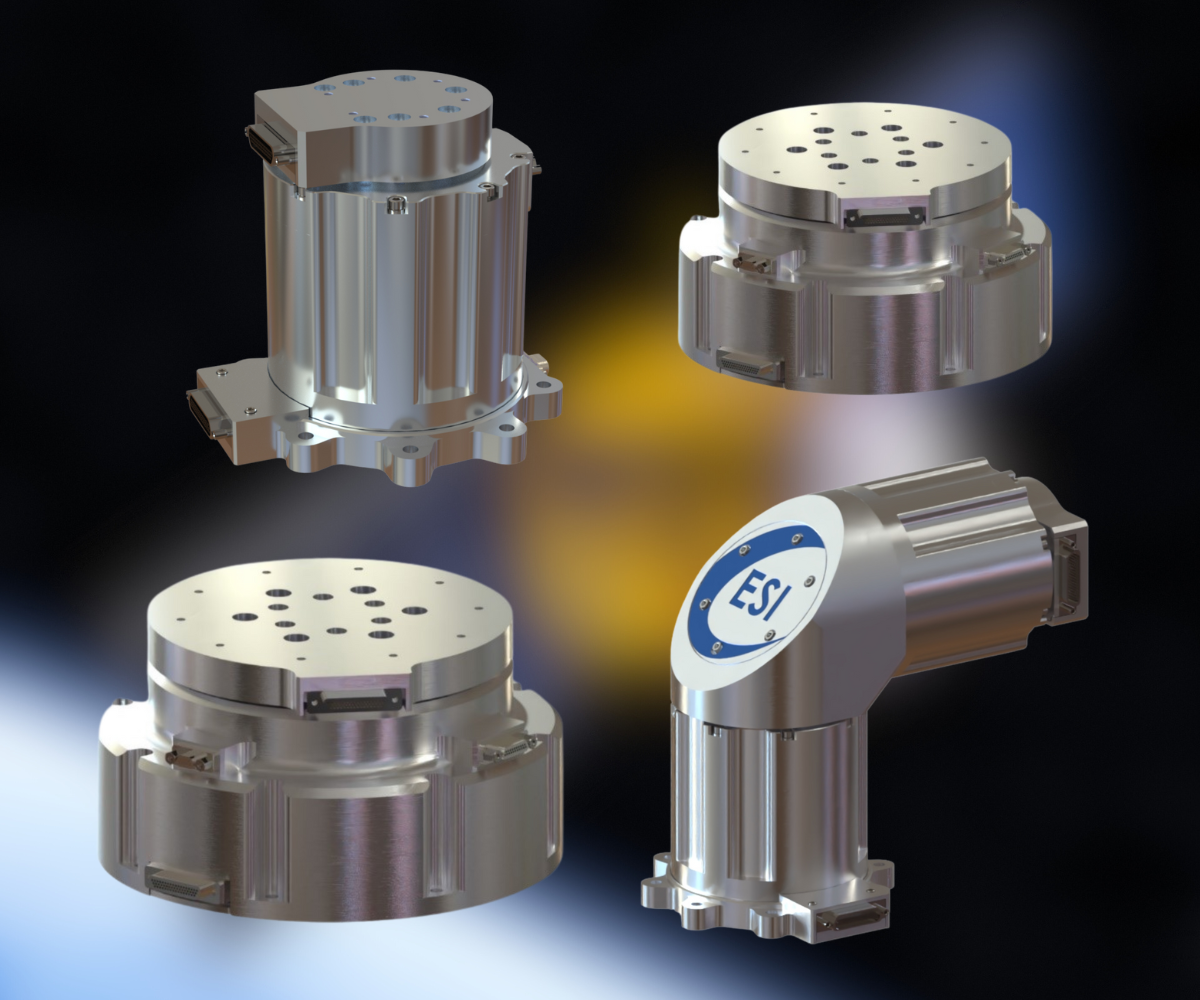
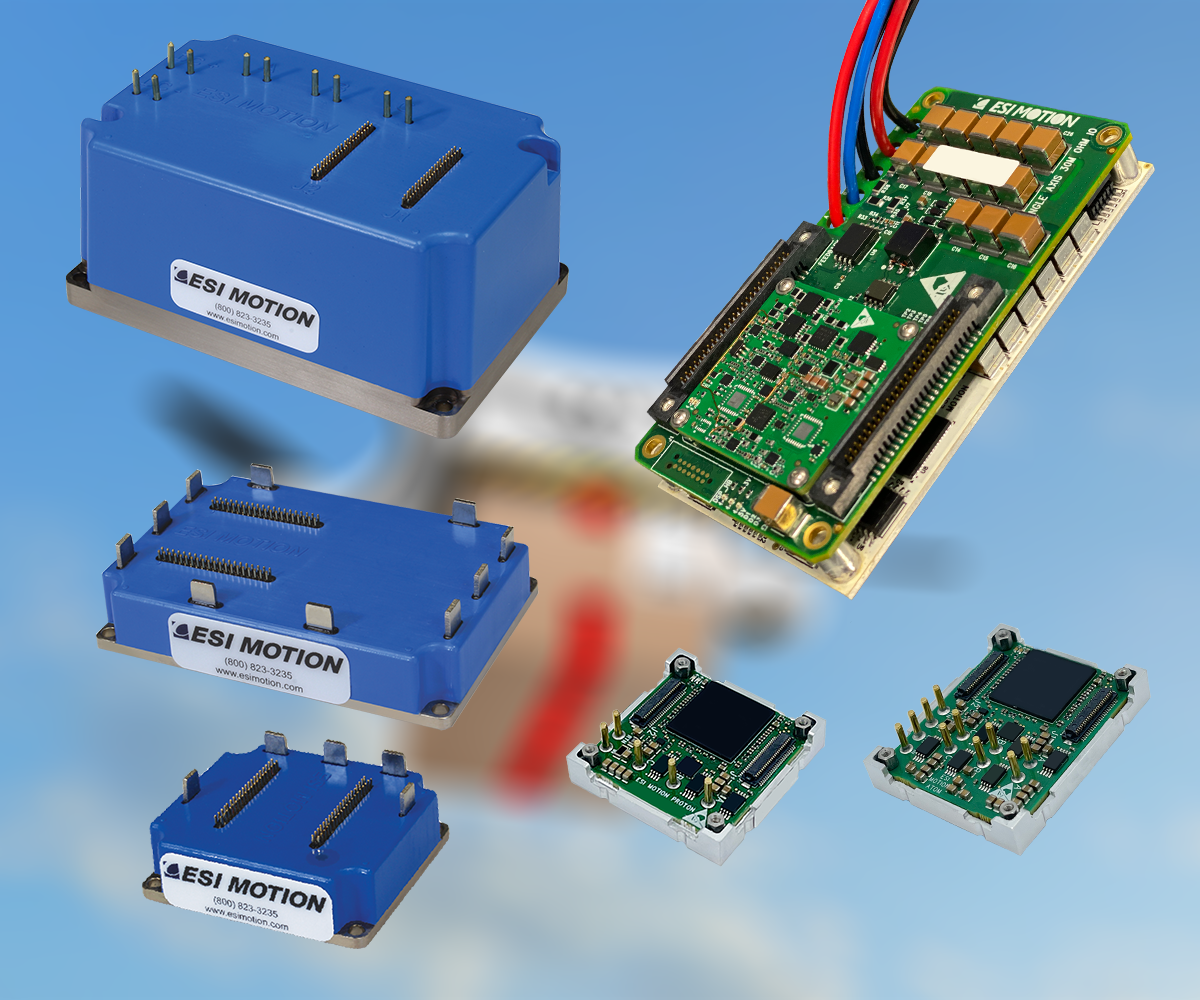
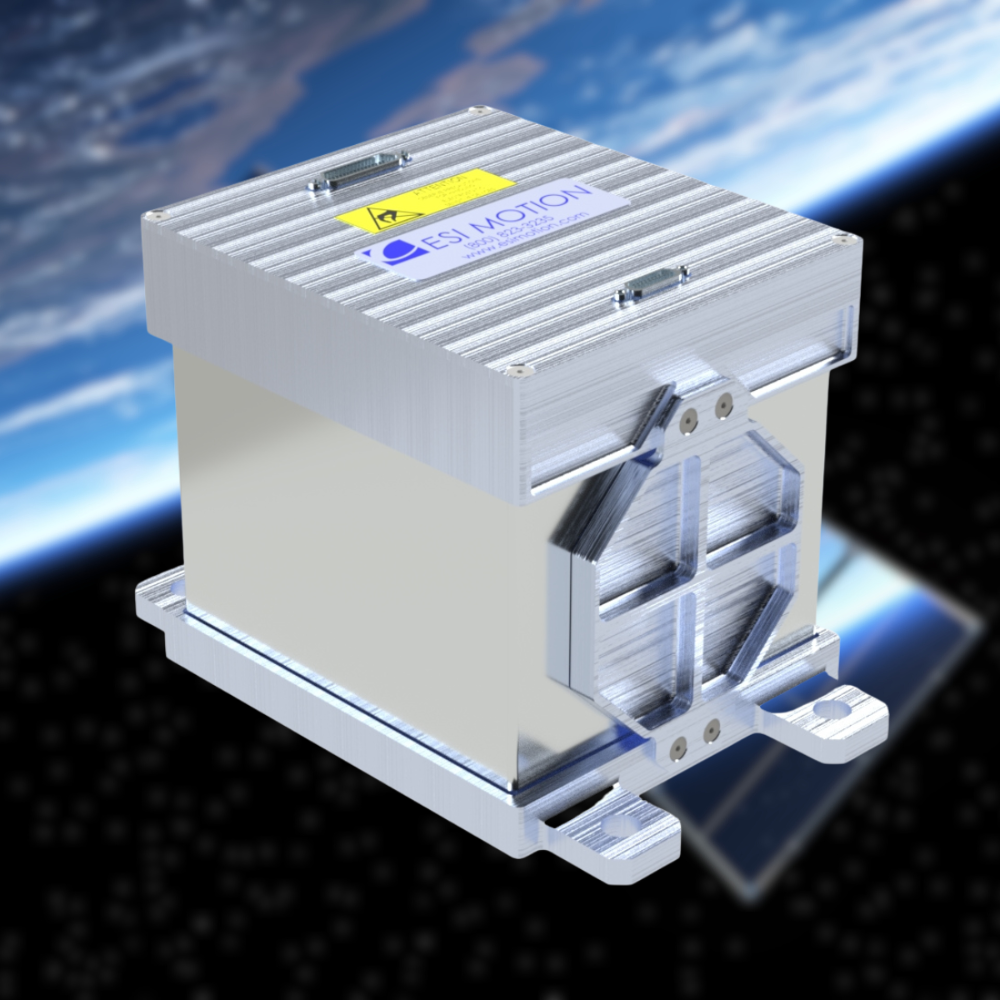
Each type of satellite is designed for specific tasks and operates in an orbit best suited to its mission. And for satellite motion control needs, ESI Motion has the Expertise and Heritage to help make the mission successful. From Positioning to Solar Array Deployment to Robotics and more, ESI offers a range of COTS Space Products depending on your needs and applications while having the ability to modify of fully customize products as well.
As an industry leader, ESI Motion possesses the know-how, experience, and support to help you achieve your mission goals while ensuring optimal performance and longevity for your equipment. ESI Motion has years of experience providing motion control for a vary of Space Applications!
Contact ESI Motion by calling +1.800.823.3235 or email us at sales@esimotion.com.
If you’ve got any questions, we’ve probably got them answered here on our FAQ. If you need any technical support, our team is here to help.
Click Here to see more of our solutions.